Sécuriser l'accès à VMware vCenter Server (VCSA) en HTTPS sous VMware vSphere 6.7
- VMware
- VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), VMware vSphere
- 25 octobre 2024 à 13:03
-

- 3/7
5. Demander un certificat auprès de votre autorité de certification sous Windows Server
Pour soumettre la demande de certificat générée depuis votre serveur VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), vous devrez vous connecter à l'interface web de votre autorité de certification sous Windows Server.
Pour cela, connectez-vous à l'adresse "https://[nom de domaine ou adresse IP du serveur où est installé le rôle Autorité de certification]/CertSrv".
Ce qui donne dans notre cas "https://ad.informatiweb.lan/CertSrv".
Utilisez le compte Administrateur de votre domaine qui, par défaut, est autorisé à inscrire (générer) des certificats en utilisant le modèle de certificat créé précédemment.
Sinon, modifiez le modèle de certificat créé précédemment et ajoutez l'utilisateur souhaité dans l'onglet "Sécurité" de celui-ci et ajoutez-lui les droits "Lecture" et "Inscrire".
Si cette interface web n'est pas disponible dans votre cas, c'est que le service de rôle "Inscription de l'autorité de certification via le Web" du rôle "Services de certificats Active Directory" n'est pas installé dans votre cas.
Si tel est le cas, installez-le et référez-vous à l'étape "Installer l'interface web de l'autorité de certification" de notre tutoriel concernant la création d'une autorité de certification racine d'entreprise (si besoin).
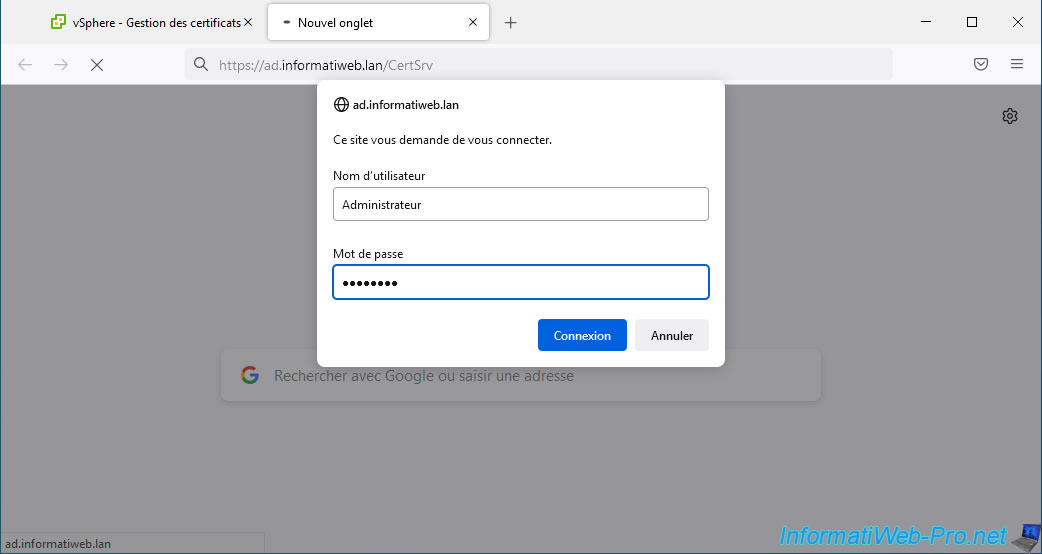
Sur la page web "Services de certificats Microsoft Active Directory - [nom de votre autorité de certification]" qui s'affiche, cliquez sur le lien "Demander un certificat".
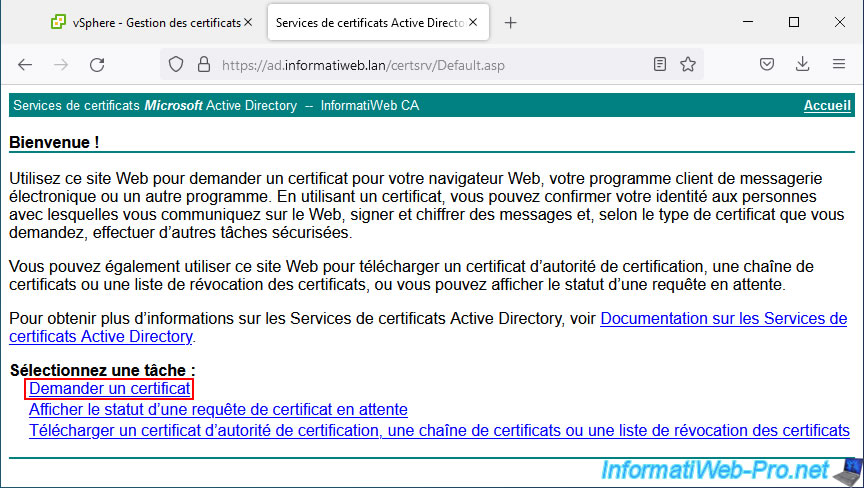
Ensuite, cliquez sur : demande de certificat avancée.

Collez la demande de certificat générée par votre serveur VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), sélectionnez le modèle de certificat "vSphere 6.x" créé précédemment et cliquez sur Envoyer.
Note : si ce modèle n'apparait pas dans votre cas :
- vérifiez que vous avez ajouté le modèle de certificat "vSphere 6.x" créé à la liste des modèles de certificats à délivrer
- dans l'onglet "Sécurité" du modèle de certificat "vSphere 6.x" créé, vérifiez que l'utilisateur que vous avez utilisé pour vous connecter à cette interface web possède au moins les droits "Lecture" et "Inscrire" pour ce modèle de certificats
- dans l'onglet "Compatibilité" du modèle de certificat "vSphere 6.x" créé sur votre autorité de certification, vérifiez que la valeur sélectionnée pour l'option "Autorité de certification" est au maximum "Windows Server 2008 R2".
- si vous possédez plusieurs contrôleurs de domaines dans votre infrastructure, il est possible que ce modèle n'ait pas encore été répliqué sur le contrôleur de domaine utilisé actuellement. Si besoin, forcez la réplication des données de votre infrastructure Active Directory.
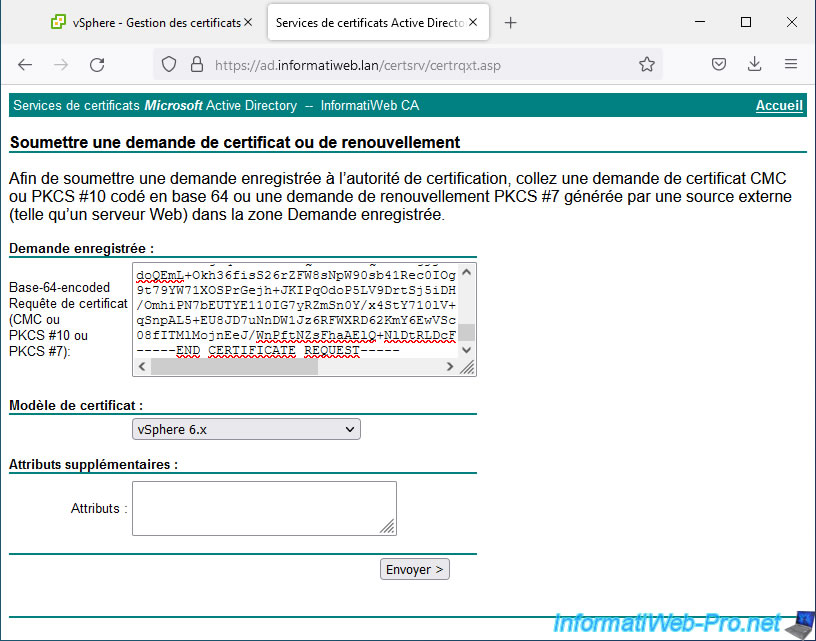
Si l'opération réussi, le message "Certificat émis" apparait.
Sélectionnez l'option "Codé en base 64" pour obtenir le certificat au format PEM et cliquez sur "Télécharger la chaine de certificats" pour obtenir le certificat émis pour votre serveur VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), ainsi que tous les certificats parents (la ou les différentes autorités de certifications parentes) pour respecter les pré-requis demandés par VMware.
En effet, si un certificat de la chaine de confiance est manquant, le certificat sera considéré comme non valide.
Votre navigateur web vous proposera de télécharger un certificat nommé : certnew.p7b.
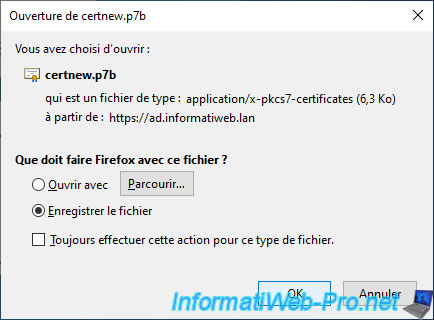
Dans notre cas, nous l'avons enregistré sous le nom : vcsa-cert-full-chain.p7b.
Comme vous pouvez le voir, Windows 10 reconnait qu'il s'agit d'un certificat PKCS #7.
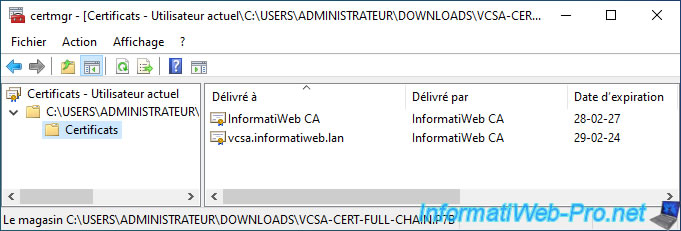
Si vous faites un double clic sur ce fichier ".p7b", vous verrez que ce fichier contient en réalité tous les certificats de la chaine de confiance nécessaires à la vérification de la validité du certificat téléchargé.
Dans notre cas, il contient 2 certificats :
- InformatiWeb CA : le certificat (sans la clé privée) de notre autorité de certification
- vcsa.informatiweb.lan : le certificat émis par notre autorité de certification "InformatiWeb CA" pour notre serveur "vcsa.informatiweb.lan".
Un peu plus tard dans ce tutoriel, vous verrez que VMware vCenter Server attend une chaine de certificats au format ".cer", ".pem" ou ".crt".
Vous devrez donc convertir ce fichier ".p7b" au format ".cer".
Pour cela, téléchargez OpenSSL, décompressez le fichier téléchargé et copie le contenu du dossier "bin" dans le dossier "C:\OpenSSL" que vous devez créer.
Ensuite, ouvrez un invite de commandes et tapez ceci pour convertir le certificat ".p7b" au format ".cer" :
Batch
cd C:\OpenSSL openssl pkcs7 -print_certs -in C:\Users\Administrateur\Downloads\vcsa-cert-full-chain.p7b -out C:\Users\Administrateur\Downloads\vcsa-cert-full-chain.cer
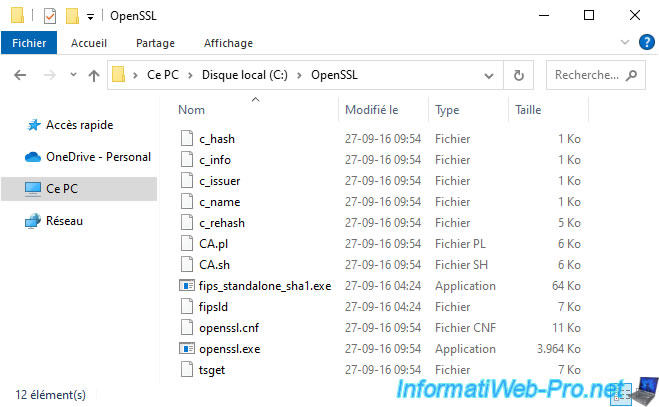
Une fois la commande OpenSSL exécutée, vous verrez un nouveau certificat au format ".cer" apparaitre à côté du fichier ".p7b".
6. Obtenir la clé privée générée par votre serveur lors de la demande de signature de certificat
Lorsque vous générez la demande de signature de certificat (CSR) depuis le client web "VMware vSphere Client" de votre serveur VMware vCenter Server, la clé privée est générée sur le disque dur virtuel de ce serveur.
Néanmoins, ce client web ne fournit pas de lien pour la télécharger facilement.
Vous devrez donc activer le protocole SSH de votre serveur VMware vCenter Server (VCSA) et vous connecter à celui-ci via PuTTY (par exemple) pour l'obtenir en ligne de commandes.
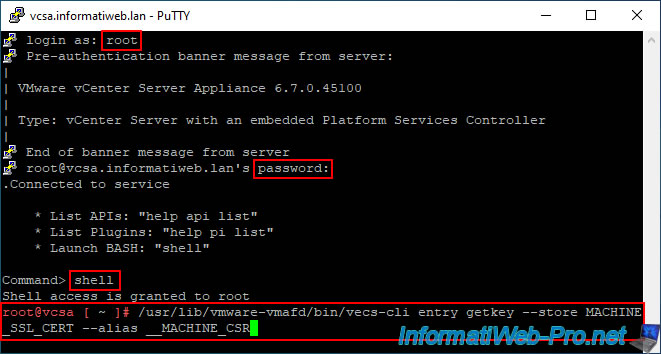
Connectez-vous en tant que root et utilisez le shell Linux en tapant la commande "shell".
En effet, par défaut, vous êtes dans le shell de l'appliance VCSA et non le Shell BASH de Linux.
Bash
shell
Ensuite, tapez la commande :
Bash
/usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vecs-cli entry getkey --store MACHINE_SSL_CERT --alias __MACHINE_CSR
Note : si vous avez un serveur VMware vCenter Server sous Windows Server, il vous suffit de remplacer "/usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vecs-cli" par "vecs-cli.exe" dans la commande ci-dessus.
Le programme "vecs-cli.exe" se trouve dans le dossier "C:\Program Files\VMware\vCenter Server\vmafdd".
La clé privée dont vous avez besoin apparait.
Copiez ce texte en incluant la ligne "BEGIN PRIVATE KEY" de début et la ligne "END PRIVATE KEY" de fin.
Plain Text
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx... -----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Note : pour copier ce texte avec PuTTY, sélectionnez le texte (et laissez-le sélectionné).
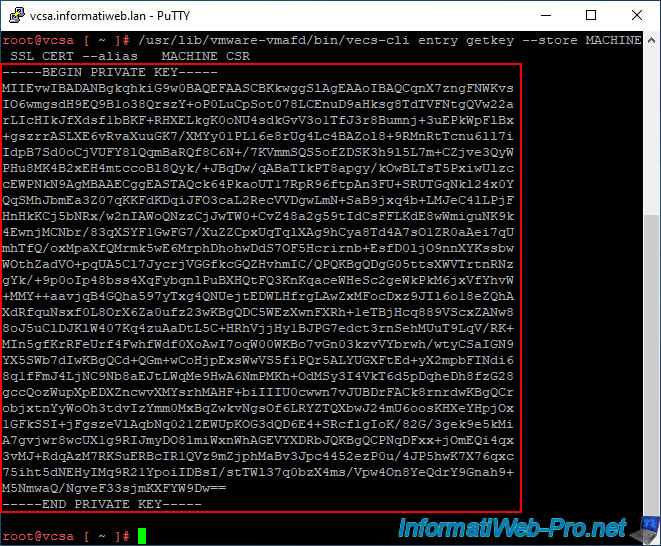
Ensuite, ouvrez le bloc-notes et collez le texte (copié automatiquement lors de la sélection de ce texte dans PuTTY).
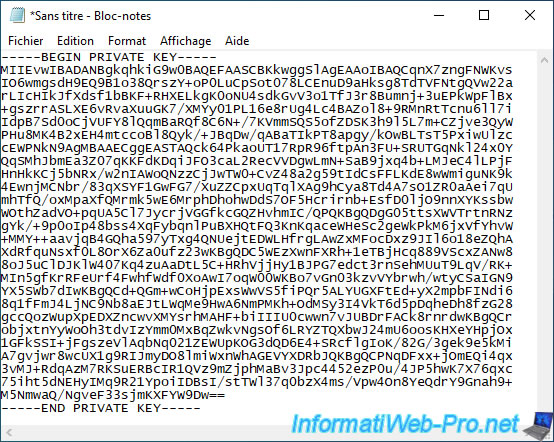
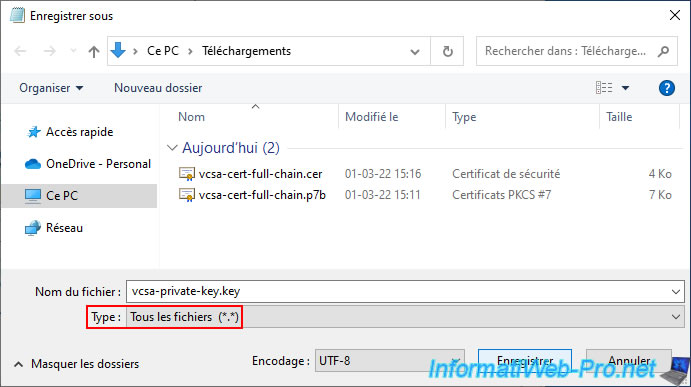
Enregistrez ce fichier texte sous le nom : vcsa-private-key.key.
5. Request a certificate from your certification authority on Windows Server
To submit the certificate request generated from your VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), you will need to connect to your certificate authority's web interface on Windows Server.
To do this, connect to the address "https://[domain name or IP address of the server where the Certification Authority role is installed]/CertSrv".
Which gives in our case "https://ad.informatiweb.lan/CertSrv".
Use the Administrator account for your domain which, by default, is allowed to enroll (generate) certificates using the certificate template created previously.
Otherwise, modify the certificate template created previously and add the desired user in the "Security" tab of it and add the "Read" and "Enroll" rights to it.
If this web interface is not available in your case, it is because the "Certificate Authority Enrollment via Web" role service of the "Active Directory Certificate Services" role is not installed in your case .
If so, install it and refer to the "Install the web interface of the certification authority" step of our tutorial on creating an enterprise root certificate authority (if necessary) .

On the "Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services - [name of your certificate authority]" web page that appears, click the "Request a certificate" link.

Then click: advanced certificate request.

Paste the certificate request generated by your VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), select the "vSphere 6.x" certificate template created previously and click Submit.
Note: if this model does not appear in your case:
- verify that you have added the created "vSphere 6.x" certificate template to the list of certificate templates to issue
- in the "Security" tab of the created "vSphere 6.x" certificate template, verify that the user you used to connect to this web interface has at least "Read" and "Enroll" rights for this template of certificates
- In the "Compatibility" tab of the "vSphere 6.x" certificate template created on your certification authority, verify that the value selected for the "Certification Authority" option is at most "Windows Server 2008 R2".
- If you have multiple domain controllers in your infrastructure, this model may not yet have been replicated to the domain controller currently in use. If necessary, force the replication of data from your Active Directory infrastructure.

If the operation is successful, the message "Certificate issued" appears.
Select the "Base 64 encoded" option to obtain the certificate in PEM format and click on "Download certificate chain" to obtain the certificate issued for your VMware vCenter Server (VCSA), as well as all parent certificates (the or the various parent certification authorities) to comply with the prerequisites requested by VMware.
Indeed, if a certificate from the chain of trust is missing, the certificate will be considered invalid.

Your web browser will prompt you to download a certificate named: certnew.p7b.

In our case, we saved it under the name: vcsa-cert-full-chain.p7b.

As you can see, Windows 10 recognizes that this is a PKCS #7 certificate.

If you double-click on this ".p7b" file, you will see that this file actually contains all the certificates from the chain of trust necessary to verify the validity of the downloaded certificate.
In our case, it contains 2 certificates:
- InformatiWeb CA: the certificate (without the private key) of our certification authority
- vcsa.informatiweb.lan: the certificate issued by our certification authority "InformatiWeb CA" for our server "vcsa.informatiweb.lan".

A little later in this tutorial, you will see that VMware vCenter Server expects a certificate chain in ".cer", ".pem" or ".crt" format.
You will therefore need to convert this ".p7b" file to ".cer" format.
To do this, download OpenSSL, unzip the downloaded file and copy the contents of the "bin" folder into the "C:\OpenSSL" folder that you need to create.
Next, open a command prompt and type this to convert the ".p7b" certificate to ".cer" format:
Batch
cd C:\OpenSSL openssl pkcs7 -print_certs -in C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\vcsa-cert-full-chain.p7b -out C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\vcsa-cert-full-chain.cer

Once the OpenSSL command is executed, you will see a new certificate in ".cer" format appear next to the ".p7b" file.

6. Obtain the private key generated by your server when requesting certificate signing
When you generate the certificate signing request (CSR) from the web client "VMware vSphere Client" of your VMware vCenter Server, the private key is generated on the virtual hard disk of this server.
However, this web client does not provide a link to download it easily.
You will therefore need to activate the SSH protocol of your VMware vCenter Server (VCSA) and connect to it via PuTTY (for example) to obtain it from the command line.

Log in as root and use the Linux shell by typing the "shell" command.
Indeed, by default, you are in the shell of the VCSA appliance and not the Linux BASH Shell.
Bash
shell
Then type the command:
Bash
/usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vecs-cli entry getkey --store MACHINE_SSL_CERT --alias __MACHINE_CSR
Note: If you have a VMware vCenter Server running Windows Server, simply replace "/usr/lib/vmware-vmafd/bin/vecs-cli" with "vecs-cli.exe" in the command above.
The program "vecs-cli.exe" is located in the folder "C:\Program Files\VMware\vCenter Server\vmafdd".

The private key you need appears.
Copy this text including the beginning "BEGIN PRIVATE KEY" line and the ending "END PRIVATE KEY" line.
Plain Text
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx... -----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Note: to copy this text with PuTTY, select the text (and leave it selected).

Then open notepad and paste the text (automatically copied when selecting this text in PuTTY).

Save this text file under the name: vcsa-private-key.key.

Partager ce tutoriel
A voir également
-

VMware 17/3/2023
VMware ESXi 6.7 - Limiter la bande passante sortante
-
VMware 25/12/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Commutateurs virtuels distribués (vDS)
-

VMware 17/5/2024
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Créer et gérer des balises
-
VMware 29/1/2025
VMware vSphere 6.7 - Surveiller trafic réseau via NetFlow

Pas de commentaire